Feature
Feature is the main entity in the engine. It is the main building block of the application.
There are two main phases of feature lifecycle, "setup" and "run"
Setup
The setup methods of all features are running in sync and are in the dependency order
Run
run Methods are running in parallel after all setup methods has finished
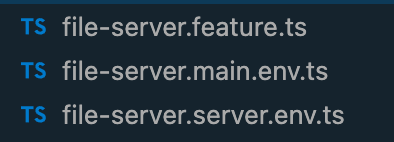
A feature is combined of several files:
<feature-name>.feature.ts- feature definition file.<feature-name>.<some-env>.env.ts- some-env specific setup code.<feature-name>.<another-env>.env.ts- another-env specific setup code.
Feature definition file
Feature definition is created in a <feature-name>.feature.ts file, and is exposed as the default export.
For example:
/* my-feature.feature.ts */
import { Feature } from '@wixc3/engine-core';
/* defining a new feature */
export default new Feature({
id: 'myFeature' /* unique id for the feature */,
dependencies: [
/* other features the feature depends on */
],
api: {
/* slots, services, and configurations of the feature */
},
});
Feature constructor accepts three options
id: string
Unique identifier, This is the feature name. For example a file-server feature will be initiated
as const fileServerFeature = new Feature({id: 'file-server', ...rest}) and the rest of the folder structure should be
prefixed with file-server.
Dependencies: []
Features that this current feature is dependant upon
api: Api
Api implements three types of interfaces:
Config
Slot
Service
Service is a method within an API. When we need to declare API methods we will call the Service.withType static.
export default class MyFeature extends Feature<'myFeature'> {
id = 'myFeature' as const;
api = {
echoService: Service.withType<() => string>().defineEntity(env1)
};
}
Feature instance
setup(env, handler)
This is the method of a feature to set itself up in an environment
arguments
| argument | description |
|---|---|
| env | the environment we want to set the feature up in |
| handler | Set up handler |
Setup handler
The setup handler is a method being called with 3 arguments.
myFeature.setup(myEnv, (settingUpFeature, dependencies, contexts) => {
// setup logic
});
- settingUpFeature - an object containing all the entities related to the feature:
| argument | description |
|---|---|
| id | (string) - id of the feature |
| run | (method) - a method will be called once this feature is ready in this environment |
| onDispose | (method) - a method will be called once this feature gets disposed in this environment |
| Own slots | (object) all the slots defined in the feature api for this environment |
| Configs | (object) all the configurations defined in the feature api and accessible in this environment |
run(cb: Function)
This will be called when the environment is ready. For example, when we want to render a react component we need the
document to be ready. In this case we will insert all react rendering logic inside the run method.
-
dependencies - a list of all the dependencies the feature declared dependency on, and all the api's available from that feature in the current environment
-
contexts - APIs provided to the specific environment in case the environment is a contextual environment.
setupContext(env, contextName,handler)
In case the environment is a contextual environment, this is how we can provide a specific context to the environment.
myFeature.setupContext(myEnv, 'envContext', (deps) => {
return {
method: () => 'from context',
};
});